How Do You Choose the Right Wheelchair to Meet Your Needs?
Time : Feb 11, 2026 表示回数 : 67

Why wheelchair selection is a system-level engineering decision, not a catalog choice
Choosing a wheelchair is not simply selecting a single product feature but a mobility system that has to perform reliably across mechanical load, posture stability, surface variation, and long-term durability. Frame geometry, wheel dynamics, braking behavior, vibration transmission, and maintenance feasibility all shape real-world performance. When any of these variables are mismatched with user conditions, the result is not inconvenience but accelerated fatigue, postural strain, reduced independence, and higher lifecycle cost.
For those engaging in procurement, clinical assessment, product evaluation, or distribution, risk does not lie in visual finish but in structural logic and design discipline. A wheelchair that appears suitable on paper may fail once exposed to ramps, curb transitions, prolonged sitting, or frequent transport cycles. This is why selection should follow design reasoning rather than catalog filtering.
This article builds a practical evaluation framework. Each section reflects how you can assess suitability based on use conditions, body mechanics, mechanical behavior, and supply reliability so that your final choice is defensible not only in theory but also in long-term application.
Why does Xunyu Medical have the ability to provide reliable products of wheelchairs?
Xunyu 医療 has evolved from a focused regional workshop into a structured manufacturer supplying mobility and elderly assistive products across international healthcare markets. Based in Danzao Town, Foshan, our company operates a 4,000-square-meter production facility dedicated to mobility and daily-living support products, including walking aids, bathroom safety devices, bedside assistance products, and 車椅子.
What differentiates Xunyu Medical is not aggressive promotion, but strict manufacturing logic. Product development follows a practical sequence—load stability first, then controllability, comfort refinement lastly. This approach reflects long-term feedback from distributors and care institutions across Europe, North America, the Middle East, and the Asia-Pacific region, where our products are now supplied through healthcare distributors and major e-commerce platforms.
Rather than framing value around hardware specifications alone, our company defines our mission around independence, safety, and dignity. As global demand grows, continued investment in design optimization, process stability, and sustainable production remains central to its strategy. This thinking of reliability over appearance aligns with how mobility equipment should be evaluated in real life.
What daily mobility scenarios will your wheelchair face in real use?
Before comparing materials or accessories, it is necessary to clarify the mechanical environment your wheelchair will operate in. Indoor hospital corridors, residential spaces, outdoor pavements, curb transitions, elevators, vehicle loading, and long ramps all impose different stress patterns on both the structure and the user.
How corridor width, turning radius, ramp gradient, and surface vibration jointly determine structural geometry, wheelbase length, and frame stiffness requirements
Narrow indoor environments require compact wheelbase geometry and predictable steering behavior, long ramps demand brake reliability and rear-wheel stability, and uneven pavement introduces vibration transmission challenges that affect both fatigue and long-term joint stress. A wheelchair selected without mapping these variables often performs well in one environment but fails in another.
How much postural support and vibration control does your body actually require?
Comfort is not defined by cushion softness but by how effectively the wheelchair distributes load through your pelvis, spine, and lower limbs while minimizing repetitive micro-shock.
Why spinal load distribution, pelvic tilt control, and shock-absorption efficiency matter more than upholstery softness in long-duration sitting
Poor pelvic support subtly alters spinal curvature over time. Repeated micro-vibration accelerates muscle fatigue and joint irritation, even when discomfort is not immediately noticeable. Structural damping, seat angle geometry, and suspension behavior influence these outcomes far more than surface padding.
For users who operate across mixed indoor and outdoor surfaces, the XY-608J マニュアル車椅子 reflects this logic by prioritizing frame balance and controlled load transfer. Its structure supports a stable posture while maintaining predictable handling under continuous minor vibration.
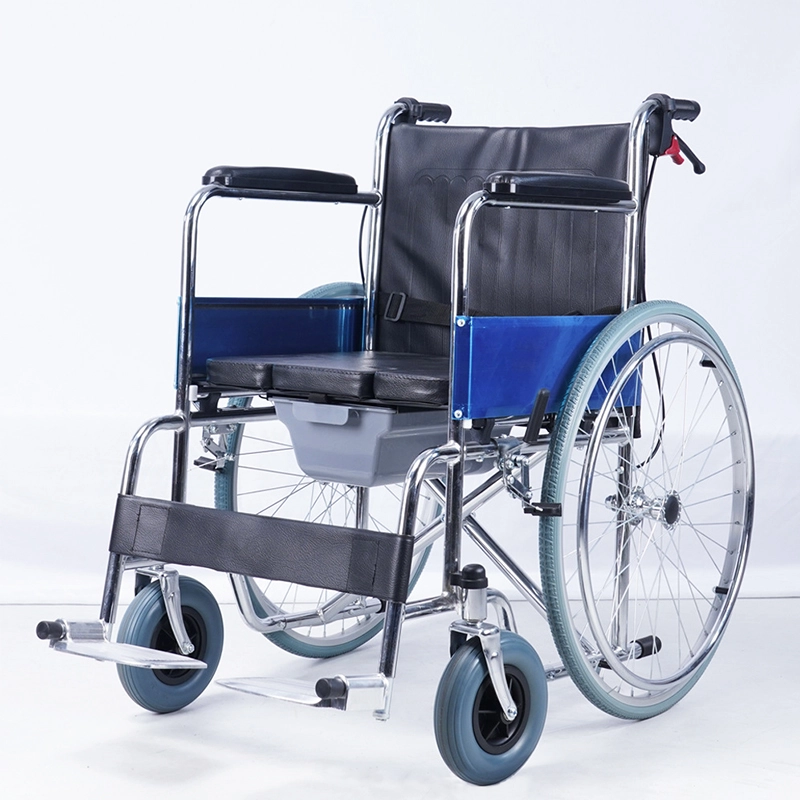

How do frame materials change durability, transport cost, and maintenance cycles?
Material choice influences not only weight but also fatigue resistance, corrosion behavior, and repair feasibility over time.
How aluminum alloy thickness, welding topology, and joint stress concentration influence service life across thousands of loading cycles
Lightweight frames with insufficient wall thickness may feel responsive initially but often degrade faster under repeated loading. Poor weld geometry concentrates stress at joints, accelerating crack development. In contrast, a structurally sound frame prioritizes balanced stress distribution rather than minimal mass alone. This distinction determines whether your equipment remains dependable after years of use or begins to fail unpredictably.
What seat dimensions prevent long-term nerve compression and circulation loss?
Incorrect seat geometry rarely causes immediate failure, but it silently degrades mobility over time.
How seat width tolerance, thigh support length, and backrest angle interact to affect blood flow and nerve pressure zones
Seat width that is too narrow increases lateral compression, seat depth that is too long impairs circulation behind the knees, and backrest angle influences pelvic tilt and spinal alignment. These parameters should be evaluated using anatomical fit rather than generic sizing categories.
How should braking systems and wheel design be evaluated for safety on slopes?
Stopping performance depends on mechanical interaction, not labeling.
Why do hand-rim friction coefficients, tire compound elasticity, and brake lever torque ratios jointly determine slope safety margins
Brake reliability is influenced by surface contact area, rubber deformation under load, and the mechanical leverage applied through the braking system. Wheelchairs used on ramps or sloped walkways must maintain predictable stopping behavior under varying user weight and speed; otherwise, safety becomes situational rather than dependable.
How do you balance portability with structural safety?
Weight reduction often comes with trade-offs. Each kilogram removed shifts the center of gravity and alters frame behavior under load.
How folding mechanisms, cross-brace geometry, and latch tolerances affect both transport convenience and frame integrity
Folding designs must maintain consistent alignment after repeated cycles. Weak latch tolerances introduce micro-movement that compounds into instability. A well-designed portable wheelchair preserves rigidity while allowing efficient transport.
For scenarios where portability must coexist with ride stability, the XY-A13-46 manual wheelchair applies a spring-based shock absorption system within a compact folding structure, reducing vibration transmission while remaining practical for frequent vehicle loading.
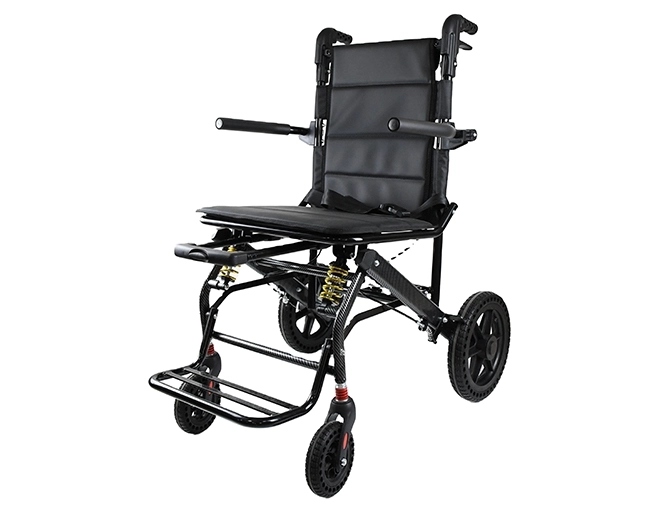

How can you verify manufacturing consistency beyond brochures?
Specifications describe intent. Manufacturing consistency determines reality.
How do factory area scale, product category breadth, export market diversity, and quality philosophy signal long-term supply reliability
A manufacturer operating structured production space, supporting multiple product categories, and serving diverse export markets demonstrates process maturity rather than short-term assembly capability. Consistency in output, rather than isolated product excellence, determines whether supply relationships remain stable over the years.
How do you evaluate the total cost of ownership instead of the purchase price?
Purchase price is only a fraction of the long-term cost.
How maintenance frequency, spare-part standardization, and structural lifespan define real annual cost
A wheelchair that requires frequent adjustment, specialized replacement parts, or premature frame repair quickly exceeds the lifecycle cost of a structurally robust model. Evaluating durability, maintenance predictability, and component compatibility offers a more realistic cost model than upfront pricing alone.
Choosing a wheelchair as a mechanical partner, not a commodity
A wheelchair is not simply equipment but a mechanical partner that supports your posture, protects your joints, manages vibration, and preserves independence across years of daily use. Effective selection begins with scenario mapping, continues through mechanical evaluation, and ends with verification of long-term reliability. When you assess geometry, load behavior, manufacturing discipline, and lifecycle cost rather than appearance, your final choice becomes technically defensible rather than speculative.
FAQについて
Q1: How often should a manual wheelchair frame be inspected for structural fatigue?
A: For daily users, a visual weld and joint inspection every 3–6 months is advisable, with a comprehensive mechanical assessment annually.
Q2: Does shock absorption meaningfully reduce long-term joint strain?
A: Yes. Continuous micro-vibration contributes to spinal and hip load accumulation even when discomfort does not appear immediately.
Q3: Is lighter always better for transport convenience?
A: Not always. Extremely light frames often compromise fatigue resistance, increasing the likelihood of structural degradation over time.