Key Design Features That Define Reliable Bed Rails for Elderly Users
Time : Feb 04, 2026 View : 15

Bed rails frequently appear as a basic item for the bedroom, but in everyday care for older people, these rails are an essential part of a broader safety system that influences the way that someone turns over or gets out of bed. For seniors whose balance, muscle strength, or quick responses have weakened, the mattress edge turns into a particularly dangerous area, particularly during nighttime hours.
A poorly designed rail sometimes generates false confidence, as it may gradually become loose or unexpectedly move while someone shifts body weight, but a carefully designed bed rail stabilizes movement, reduces worry, and brings down the chance of falling while maintaining users’ independence. The article centers on specific design elements that determine whether a bed rail continues to function reliably after long periods of actual everyday use.
Why is a bed rail a safety tool rather than a simple support bar?
A bed rail does more than offer something to hold onto.
How does it reduce fall risk?
Whenever an individual turns in bed or moves into a sitting posture, the rail offers a steady reference point, which helps prevent uncontrolled sliding toward the side of the bed and provides useful leverage at the beginning of the standing process. Consequently, sudden changes in weight distribution occur less often, and body alignment remains under better control in low-visibility conditions.
Why does psychological safety matter?
Mobility at night depends heavily on the users’ confidence. When the person feels certain that solid support exists near the bed edge, moments of hesitation grow fewer, and movements then become deliberate. Such conditions reduce abrupt reactions driven by fear, so sudden steps or awkward twists, which commonly lead to loss of balance, happen less frequently.
What structural features define real stability?
Stability begins with geometry and materials.
Why does base length affect safety?
The base of a bed rail acts as a counterweight system beneath the mattress. A short base creates a narrow support polygon, increasing the chance of rotation when force is applied to the handrail. A longer base spreads the load across a wider area, lowering the tipping moment during standing or sitting transfers.
How does the frame material influence rigidity?
Carbon steel frames resist bending under repeated stress better than thin-wall alloys or light tubing. Wall thickness and joint welding quality determine whether the rail maintains alignment after hundreds of loading cycles. Gradual deformation is often invisible but directly affects balance during use.
How does the installation method affect daily usability?
Even the strongest structure fails if installation is complex or inconsistent.
Why does tool-free installation matter?
In home environments, rails are frequently installed by family members rather than technicians. Systems that require no tools lower the risk of mistakes during assembly and ensure that the correct positioning of the base beneath the mattress becomes more consistent. These designs also make removal and installation easier after cleaning or furniture rearrangement.
How does a detachable design support flexibility?
Detachable frames allow the rail to be moved between rooms, stored during travel, or temporarily removed for medical procedures. This flexibility prevents improvised solutions, such as using furniture or unstable grab points, that introduce new risks.
How do we handle shape and surface affect grip reliability?
The handrail is the most frequently loaded component.
Why does foam grip improve safety?
Surfaces covered with foam material enhance the friction, which is especially valuable for individuals whose hand strength has weakened or who have arthritis. Foam also cushions the contact with cold metal in winter and reduces localized pressure on finger joints. Therefore, users sustain their grip for a longer time without becoming tired so quickly.
How does the flat tube design protect the body?
Flat tubing distributes pressure over a broader surface when the user leans backward or sideways. Compared with round tubes, it reduces the chance of concentrated discomfort along the spine or ribs during prolonged sitting at the bed edge.
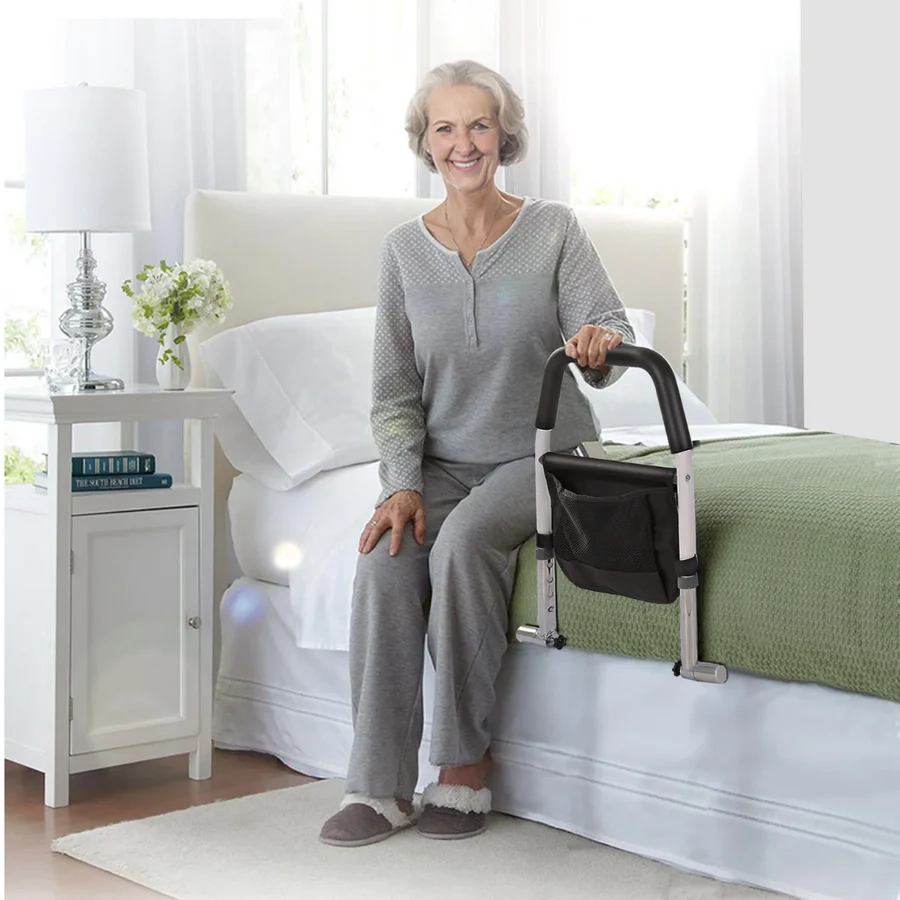
What type of bed rail suits basic home assistance?
Not every situation requires a heavy, floor-standing structure.
When is a compact bedside assist rail enough?
When the user manages to stand without help but requires some assistance to rise, a smaller assist rail often meets the need. These models emphasize a modest space requirement along with simple placement procedures while still delivering a safe handhold.
A typical example is the XY-316 bedside assist rail, which uses a carbon-steel main frame, flat-tube structure, foam grip, and tool-free detachable installation to support daily transfers in small bedrooms. The design reflects a balance between portability and rigidity, with a base length sized to fit beneath standard mattresses and a load capacity suited for light-to-moderate assistance scenarios.
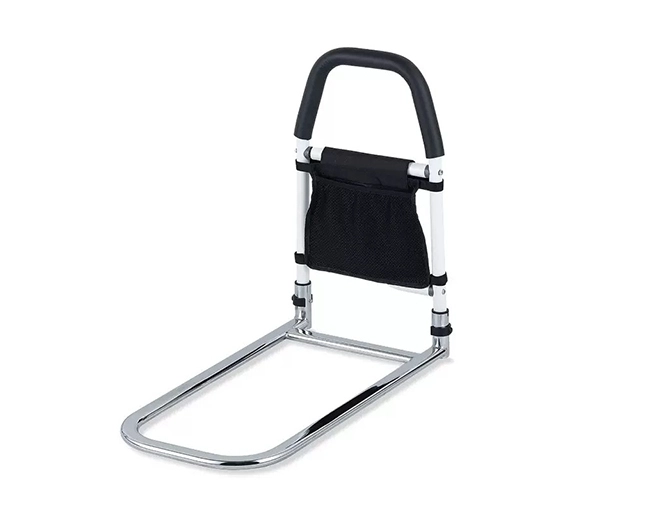

When do you need a heavier-duty bed rail?
As mobility declines, structural margins become more important.
How does adjustable height improve usability?
Bed frames differ in thickness, and mattress depths vary considerably. Rails with adjustable height position the grip at a level that matches the user’s typical elbow placement, thus reducing the shoulder tension and improving the efficiency of upward pushing during standing.
Why does load capacity define long-term safety?
During assisted transfers, the rail may briefly carry a significant portion of body weight. A higher rated capacity provides a buffer against fatigue in joints and welds, preserving rigidity over time.
The XY-429 bed rail illustrates this category, with a floor-standing design, extended base length, multi-level height adjustment, foam handle, flat-tube reinforcement, and anti-slip foot pads. Its specified load capacity reaches 136 kg, and the widened base increases resistance to lateral movement during high-force transfers.
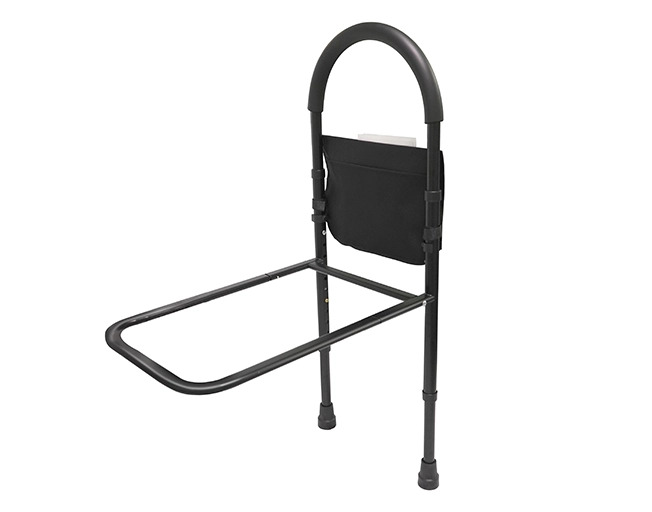

How do small design details reveal real-world usability?
Minor features often determine whether a product integrates smoothly into daily routines.
Why does a storage pouch matter?
Keeping glasses, medication, or a phone within arm’s reach reduces nighttime walking. Fewer trips across the room mean fewer exposure moments to imbalance or poor lighting.
How does an anti-slip foot pad protect stability?
Floor-standing rails rely on friction to prevent drift. Rubberized foot pads absorb micro-movement during weight shifts and maintain consistent contact on smooth flooring, preventing gradual migration away from the bed.
Who is Xunyu Medical in the field of elderly assistive devices?
Xunyu Medical operates a production facility of about 4,000 square meters dedicated to assistive equipment for older adults. Our product portfolio includes bed rails, walkers, shower chairs, bedside commodes, toilet armrests, and toilet risers, all developed with a focus on functional safety and ease of use.
Since the establishment of our company, we have emphasized technological refinement to adapt designs to real mobility limitations. Today, our products are supplied to healthcare distributors and major e-commerce platforms across Europe, North America, the Middle East, and the Asia-Pacific region.
How do you balance cost, durability, and long-term risk?
The initial price rarely reflects the full ownership cost.
What usually fails first in low-quality rails?
Common weak points involve base connections that slowly loosen, protective layers that wear thin and gradually corrode, and hardened foot pads that lose friction. These problems accrue quietly and undermine the stability before the changes become obvious.
Why does durability reduce caregiver burden?
A rigid, predictable structure minimizes the need for constant monitoring. Family members and caregivers can rely on consistent performance, which reduces anxiety during nighttime assistance and limits emergency interventions.
Conclusion
Reliable bed rails are defined less by appearance and more by structural geometry, material quality, and attention to everyday usage patterns. Base length determines tipping resistance, frame material governs long-term rigidity, and handle design shapes how safely force is transferred during standing.
When selection is guided by user mobility, bedroom layout, and assistance level rather than catalog images alone, the rail becomes a stable extension of the bed environment. It supports autonomy, lowers accident probability, and helps preserve dignity in routine movements that would otherwise carry significant risk.
FAQs
Q1: How do you know whether a basic bed rail is enough?
A: If the user can stand independently and only needs light leverage, a compact assist rail is suitable. When balance is unstable, or assistance is frequent, a heavier structure offers better safety margins.
Q2: Does adjustable height really matter?
A: Yes. Proper alignment with bed height and user stature improves leverage and reduces joint strain during transfers.
Q3: How often should a bed rail be replaced?
A: Replace it when looseness, sliding, or visible deformation appears. A well-built rail can remain reliable for several years under normal daily use.