What Key Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting a Wheelchair?
Time : Dec 10, 2025 View : 671
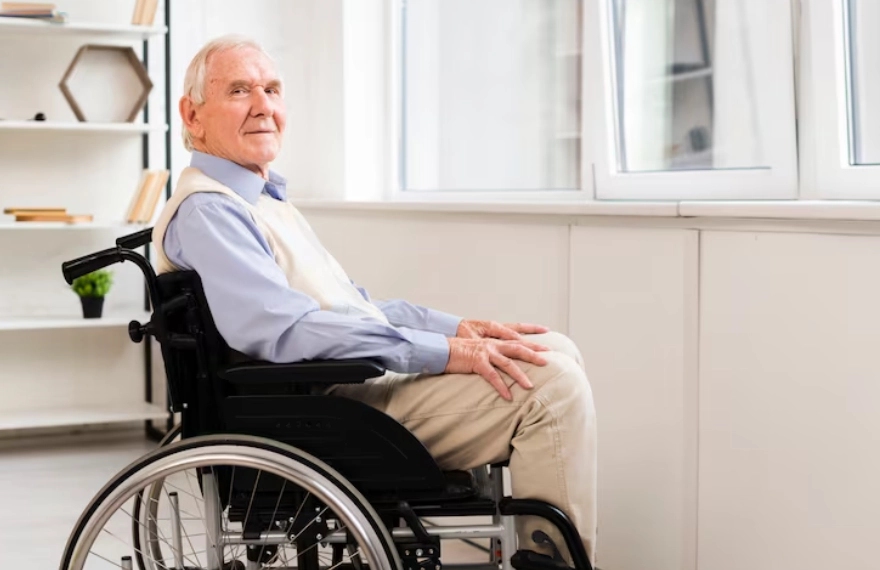

Choosing the correct wheelchair requires careful personal evaluation because no single model fits everyone. The process starts by picking the proper kind, such as transport chairs or standard manual chairs, according to the user’s movement ability, daily environment, and health conditions. It is quite essential to exactly measure the user’s seat width, seat depth, back height, and distance from seat to floor so as to have good posture, enjoy comfort and avoid injury. Additional parts including armrests, footrests, and special seat pads have to meet the user’s needs to provide better support and easier handling. Lastly, all these pieces must work together as one complete system that supports the person’s normal activities, encourages freedom, and keeps safety and comfort for many years.
Why is One-Size-Fits-All Wheelchair Almost “Impossible”?
The Importance of Personalization in Wheelchair Selection
No single wheelchair works perfectly for every person, and this fact creates difficulty when searching for the right one. A basic model might be acceptable for rare or brief trips. However, anyone who sits in wheelchair for hours every day needs a seating system that is exactly for his or her body shape and address daily tasks.
Simple stock chairs can move patients short distances inside a building, yet long-term users require custom sizes and features. A carefully chosen wheelchair must fit the shape of body , frequency of utilization, the applicable places (inside rooms or outside paths), and the health of users. Proper wheelchiars can help improve sitting posture, lower the chance of skin sores, and make operation easier.
Steps in Selecting a Proper Wheelchair
The first taskis to decide the type of wheelchair which fits the user best. This choice depends on medical problems, movement goals, and normal lifestyle. Next, workers must take careful body measurements so the seat fits without squeezing or leaving extra empty space. These numbers help avoid many common posture troubles. After that, the framecan become a full mobility and seating answer with appropriate armrests, leg supports, cushions, and height settings.
Understanding Different Types of Wheelchairs and Corresponding Applications
Transport Wheelchairs
Transport wheelchairs own light frames and small back wheels so another person can push them easily. Caregivers move the user because the wheels are not made for self-pushing. These chairs serve short rides and fold quickly for car travel.
Lightweight Manual Wheelchairs
Lightweight manual chairs fold fast and weigh little, so lifting them into vehicles becomes simple. Many parts swing away or adjust in height. They work well for occasional travel but may wear out under constant hard use.
Standard Manual Wheelchairs
Standard manual wheelchairs appear most often in homes and care centers. Great quality and higher weight capacity make them suitable for daily indoor and outdoor movement when folding size is not very importent.
Heavy-Duty Wheelchairs
Heavy-duty wheelchairs carry additional steel in every stressed place so as to support heavier users in a safe way. Although bigger size reduces easy transport, the strong structure brings needed steadiness for long-term sitting.
Reclining Wheelchairs or Tilt Wheelchairs
Reclining wheelchairs or tilt wheelchairs make the seat back lean far backward or the whole seat tilt while keeping the same leg angle. These movements spread body pressure in new ways and help users who cannot hold their back straight.
Bariatric-Specific Wheelchairs
Bariatric-specific wheelchairs use the thickest steel and widest seats among all types. Extra-wide bases plus custom cushions give safe support for people with larger body shapes.
How to Accurately Measure for Proper Wheelchair Fit?
Seat Width
Workers measure across the widest part of the hips or thighs while the person sits straight. They add one inch for normal clothing. When side cushions are planned, the thickness of both cushions is added to the final number.
Seat Depth
Measurement runs from the back of the buttocks to the bend behind the knee. Workers subtract about two and a half inches so the edge does not press the knees. If a thick back cushion will be used, its thickness is added back.
Back Height
The tape measure goes from the sitting surface up to the bottom of the stretched arm. Half the seat cushion thickness is added. For users with strong back muscles, four inches are subtracted. For weaker trunk control, only three inches are taken away.
Seat-to-Floor Height
Users should choose the right one according to their height. People shorter than 5′5″ usually need Hemi height around 17½ inches from seat to floor so feet can touch and help push.
People between 5′5″ and 6′2″ fit adult height of 19½ to 20½ inches.
Anyone taller than 6′2″ needs tall models with 21½ inches seat height.
Functional Features and Accessories That Enhance Usability
Armrest Options
Full-length armrests reach far forward and make standing up easier. Desk-length armrests stop shorter so the wheelchair slides under tables. Flip-back or height-adjustable armrests move out of the way during side transfers.
Leg Support Systems
Swing-away footrests turn sideways for safe transfers. Elevating legrests lift the whole lower leg and include soft calf pads for users who must keep legs raised.
Seat Cushioning and Back Support Materials
Cushion Options
Vinyl covers clean quickly and last long, while nylon fabric lets air pass through and feels cooler during hot weather.
Backrest Considerations
Backrest fabric must stay strong yet allow air flow so the user does not overheat during long sitting periods.
Adjustable Seat Heights & Dual-Axle Design
Dual-axle frames let the seat drop several inches lower. Shorter users can then touch the floor with their feet and help push the wheelchair.
Structural Strength & Durability Considerations
Users should choose the proper one based on the frequency of utilization. Light indoor movement only needs simple lightweight frames. For smoother rides inside buildings, XY-A13–46 includes spring shock absorbers under the seat.
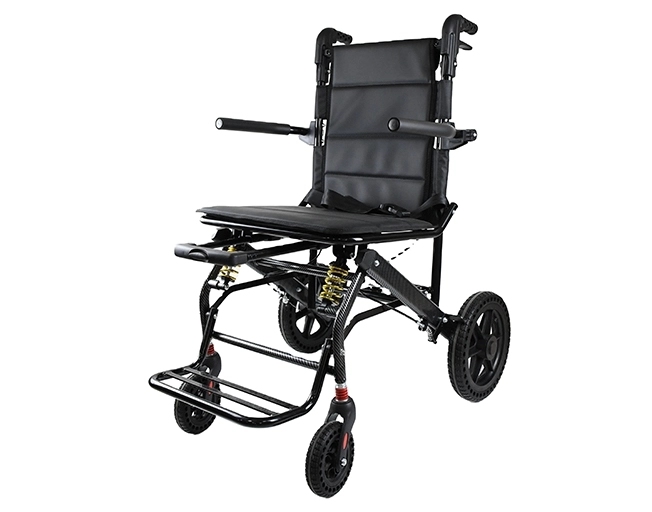

Outdoor paths and rough ground demand stronger build. The XUNYU 12-inch dual shock absorption wheelchair carries honeycomb tires and double reinforcement for tough surfaces.
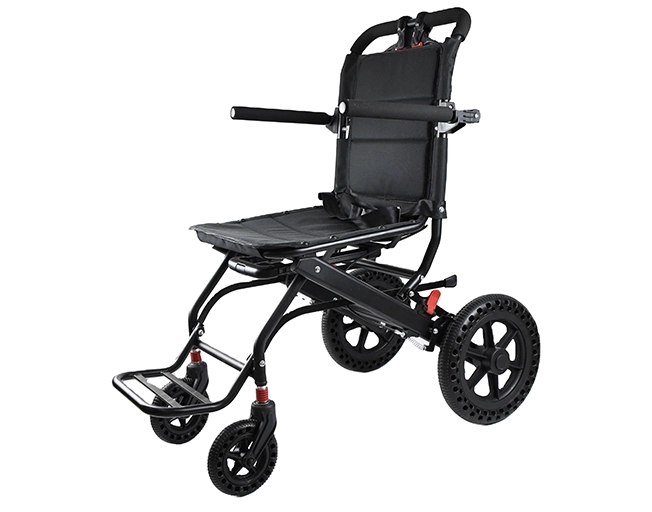

Selecting a Wheelchair as a Complete Seating System Solution
Integrating Cushions, Positioning Aids & Accessories
A plain frame becomes a true medical seating system only when proper cushions, side supports, belts, and headrests are added. Good cushions spread weight evenly and stop pressure sores. Extra pads and straps keep the body in safe alignment when muscles are weak.
Matching Functionality With Lifestyle Needs
Daily habits decide many details. Some users travel far outside and need large wheels plus strong shock absorbers. Others stay mostly inside narrow rooms and choose compact folding frames with swing-away parts. The difference between self-pushing and caregiver pushing also changes wheel size and frame weight.
FAQs
Q1: How do I know which XUNYU wheelchair model is right for my patient?
A1: Look at body weight, remaining arm strength, main locations of use, and need for self-movement. The XY-A13–46 works well for lighter users who stay mostly indoors and want soft spring suspension. The 12-inch dual shock absorption model serves active users who face rough outdoor ground.
Q2: Can I adjust XUNYU wheelchairs after purchase?
A2: Most XUNYU MEDICAL models allow later changes to armrest height, leg-rest angle, back tension, or seat height through dual-axle settings, so the chair can grow with changing needs.
Q3: What if my patient’s measurements fall between two sizes?
A3: Choose the slightly larger size, especially in seat width, to leave room for winter clothes or future cushions while still keeping good posture control. Contact XUNYU MEDICAL staff for exact advice when measurements are close.